X chromosome reactivation: the Mechanisms
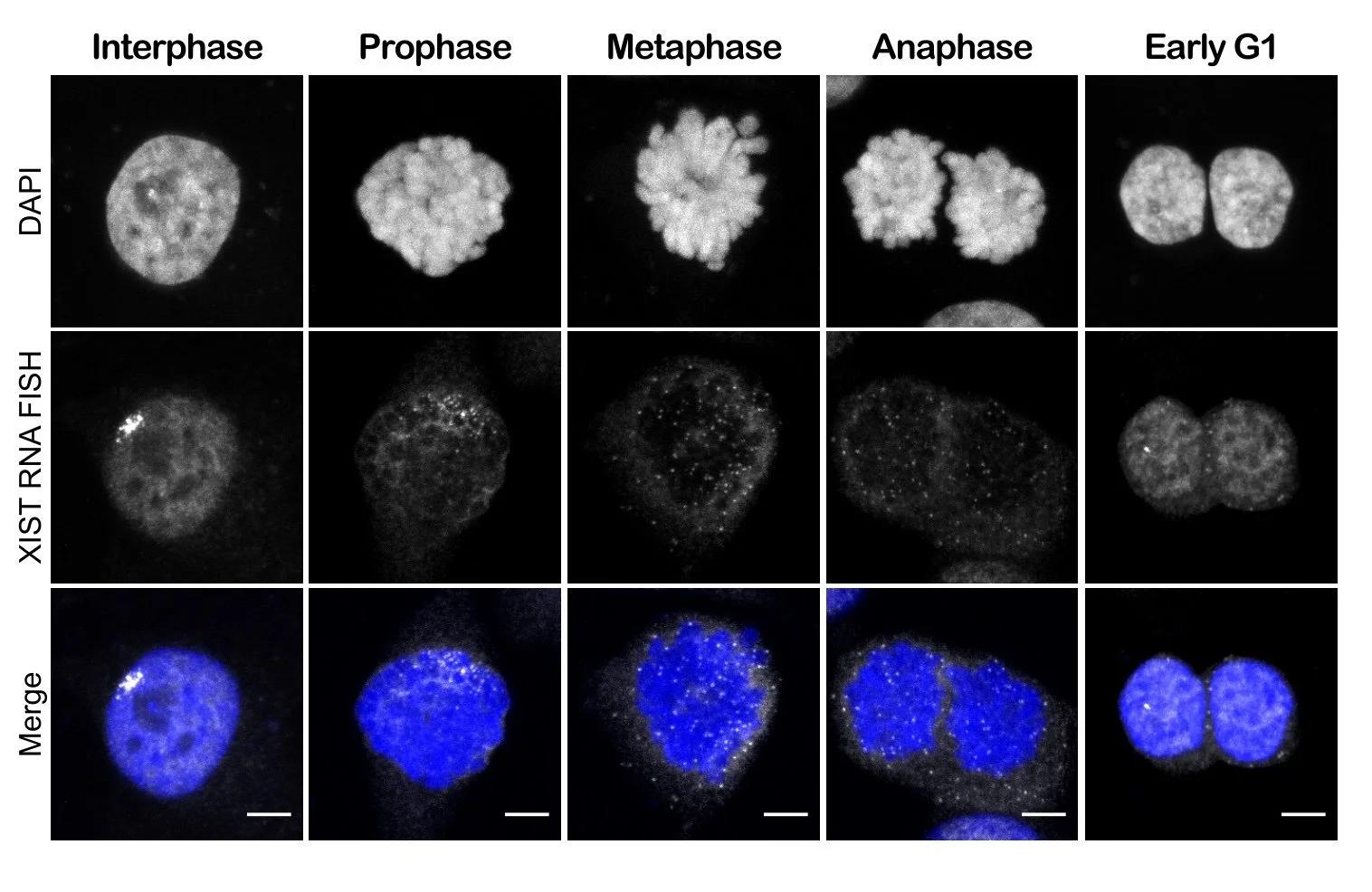
We study the X as an epigenetic exemplar and want to understand whether and how silencing at Xi genes can be reversed. My key discovery shows that the delocalization of XIST long non-coding RNA from the Xi chromosome territory is tightly associated with the reactivation of genes during cell reprogramming. As XIST delocalises at every mitosis, one of our projects investigates whether mitosis is a window of opportunity for stochastic transcriptional events to occur under normal and/or perturbed conditions, and their potential inheritance. In particular, we have identified a family of transcription factors that bind Xi reactivated genes and we are investigating the role of these TF in inducing Xi transcription at the exit of mitosis.
XIST delocalization during cell fusion-mediated somatic cell reprogramming is associated with Xi gene reactivation (Cantone I, Phil Trans of Royal Society 2017)
XIST delocalization during somatic cell cycle (modified from Cantone et al., Nature Comm 2016)
Cantone I* (corresponding author), Dharmalingam G, Chan YW, Kohler AC, Lenhard B, Merkenschlager M and Fisher AG. Allele-specific analysis of cell fusion-mediated pluripotent reprogramming reveals distinct and predictive susceptibilities of human X-linked genes to reactivation. Genome Biol. 2017 Jan 25;18(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s13059-016-1136-4.
Cantone I, Bagci H, Dormann D, Dharmalingam G, Nesterova T, Brockdorff N, Rougeulle C, Vallot C, Heard E, Chaligne R, Merkenschlager M, Fisher AG. Ordered chromatin changes and human X chromosome reactivation by cell fusion-mediated pluripotent reprogramming. Nat Commun. 2016 Aug 10;7:12354. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12354.